2025년 중국의 미세먼지 대응 상황과 실제 현실
The Situation Regarding Fine Dust in China in 2025
2025년 중국 내 미세먼지 상황은 정부의 야심찬 저감 정책에도 불구하고 여전히 심각한 환경 위협으로 남아있음.
The fine dust situation in China in 2025 remains a serious environmental threat despite the government's ambitious reduction policies.
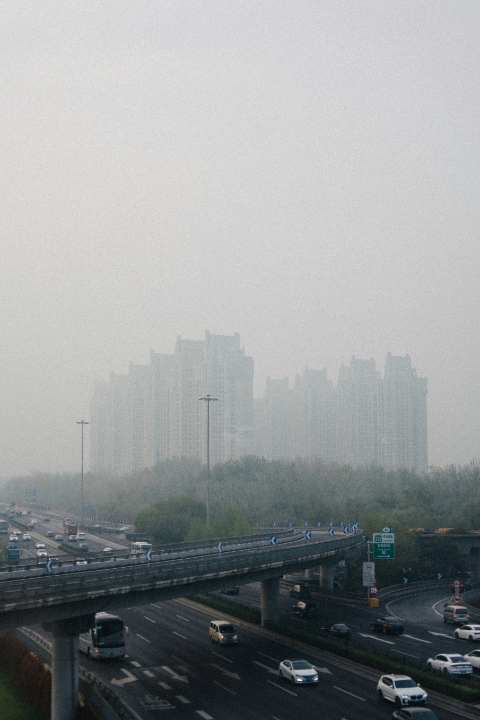
중국 정부가 2023년 발표한 '대기질 지속 개선 행동계획'에 따라 2025년까지 초미세먼지(PM2.5) 농도를 2020년 대비 10% 줄이는 목표를 설정했지만, 몽골과 네이멍구에서 발원한 황사가 베이징을 강타하며 PM10 농도가 800~1,000μg/㎥까지 치솟는 상황이 발생했음.
Severe sandstorms originating from Mongolia and Inner Mongolia hit Beijing, driving PM10 levels to an alarming 800–1,000 μg/㎥, despite the Chinese government's goal to reduce PM2.5 levels by 10% compared to 2020 under the "Action Plan for Continuous Air Quality Improvement" announced in 2023.
이는 중국의 미세먼지 저감 정책과 실제 대기환경 사이의 간극을 보여주는 사례로, 중국 내 미세먼지 문제의 복잡성과 해결의 어려움을 명확히 드러냄.
This highlights the gap between China's fine dust reduction policies and the actual air quality, clearly demonstrating the complexity and challenges of addressing fine dust issues in the country.
중국 미세먼지 저감 목표와 정책
China's Fine Dust Reduction Goals and Policies
중국 국무원은 2023년 '대기질 지속 개선 행동계획'을 발표해 2025년까지의 대기질 개선 목표와 방안을 제시했음. 이 계획은 야심찬 목표를 담고 있으며, 주요 내용은 다음과 같음.
In 2023, China's State Council announced the "Action Plan for Continuous Air Quality Improvement," outlining goals and measures for air quality improvement by 2025. This plan includes ambitious targets, as detailed below.
주요 감축 목표
Key Reduction Targets
- 초미세먼지(PM2.5) 농도: 2020년 대비 10% 이상 감축
- Reduce PM2.5 concentration by over 10% compared to 2020
- 질소산화물(NOx) 및 휘발성유기화합물(VOCs) 총 배출량: 2020년 대비 10% 이상 감축
- Reduce total emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by over 10% compared to 2020
- 징진지(베이징·톈진·허베이) 및 주변 지역 PM2.5 농도: 2020년 대비 20% 감축
- Reduce PM2.5 concentration in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (Jing-Jin-Ji) and surrounding areas by over 20% compared to 2020
- 펀웨이평원 지역: 2020년 대비 15% 감축
- Reduce PM2.5 concentration in the Fenwei Plain region by over 15% compared to 2020
특히 수도권이라 할 수 있는 징진지 지역은 더 높은 감축 목표를 설정했으며, 이는 이 지역이 중국에서 미세먼지 문제가 가장 심각한 곳 중 하나라는 점을 고려한 것으로 보임.
Higher reduction targets were set for the Jing-Jin-Ji region, which is considered a metropolitan area, acknowledging that this region faces some of the most severe fine dust problems in China.
구체적인 실행 방안
Specific Implementation Plans
중국 정부는 이런 목표를 달성하기 위해 몇 가지 핵심 전략을 내놓았음.
The Chinese government has introduced several key strategies to achieve these goals.
- 산업구조 조정: 신규 철강 생산설비 금지, 노후 생산설비 철거 추진
- Industrial restructuring: Ban on new steel production facilities and promote dismantling outdated facilities
- 에너지믹스 개선: 비화석에너지 비중을 약 20%로 확대
- Improve energy mix: Increase the share of non-fossil energy to approximately 20%
- 석탄 소비 감축: 징진지 및 주변지역 석탄 소비량을 약 10% 감축
- Reduce coal consumption: Cut coal consumption by about 10% in the Jing-Jin-Ji region and surrounding areas
- 교통구조 개선: 철도 화물 운송량 증대, 신에너지차(NEV) 확대
- Improve transportation structure: Increase rail freight transport and expand the use of new energy vehicles (NEVs)
- 오염관리 강화: 건축 부문 개선, 노천 광산 제한
- Strengthen pollution control: Improve construction practices and restrict open-pit mining
특히 교통 부문 저탄소 녹색 전환에 관한 내용이 많았는데, 이는 북부지역 초미세먼지 증가의 주요 원인인 질소산화물 배출원이 자동차와 같은 이동오염원이기 때문임.
Significant emphasis was placed on achieving low-carbon green transitions in the transportation sector since mobile pollution sources like automobiles are major contributors to nitrogen oxide emissions, which drive PM2.5 increases in northern regions.
현실 상황: 정책과 현실의 괴리
Current Reality: The Gap Between Policy and Reality
야심찬 목표에도 불구하고, 현재 상황을 보면 여전히 미세먼지와 황사 문제가 심각함. 여러 복합적인 이유가 있음.
Despite ambitious goals, the current situation shows that fine dust and sandstorm issues remain severe due to various complex reasons.
최근 황사와 미세먼지 사태
Recent Sandstorm and Fine Dust Incidents
몽골과 중국 네이멍구 지역에서 돌풍으로 황사가 발원하며 베이징의 PM10 농도가 치솟는 일이 발생했음. 황사의 영향을 받는 동안 PM10 농도는 최고 800~1,000μg/㎥까지 오르기도 했음. 이는 '매우 나쁨' 단계 기준을 훨씬 초과하는 수치임.
Severe sandstorms originating from Mongolia and Inner Mongolia caused PM10 levels in Beijing to surge dramatically during their impact, reaching as high as an alarming 800–1,000 μg/㎥—far exceeding the "very poor" air quality threshold.
또한, 네이멍구에서 발생한 황사가 발해만 인근 모래 먼지와 합쳐져 남쪽으로 이동하며 한국에도 영향을 미침. 이로 인해 인천과 충청 지역의 미세먼지가 '매우 나쁨' 단계까지 올라갔다는 보고가 있음.
Additionally, sandstorms from Inner Mongolia combined with dust near Bohai Bay and moved southward, impacting South Korea. Reports indicate that fine dust levels in areas like Incheon and Chungcheong rose to "very poor" levels as a result.
정책 실현 가능성에 대한 의문
Questions About Policy Feasibility
중국의 에너지 부족 문제는 석탄 사용 증가로 이어지는 패턴을 보여왔음. 예를 들어 석탄 수입량은 역대 최다 규모를 기록하기도 했으며 이는 에너지 안보 문제와 맞물려 있음. 봄철 황사 현상은 자연적 요인이라 완전히 통제하기 어려운 문제도 있음.
China's energy shortages have led to increased coal usage patterns—for instance, coal imports have reached record highs due to energy security concerns. Additionally, spring sandstorms are natural phenomena that are difficult to fully control.
중국 미세먼지 저감 노력의 사례와 평가
Examples and Evaluation of China's Efforts to Reduce Fine Dust
도시 녹화를 통한 저감 노력
Efforts Through Urban Greening
베이징시는 푸싱루 등에서 녹화 사업을 추진했으나 식생 배치와 수종 선정이 미흡해 효과가 제한적이었다는 평가가 있음.
Beijing has promoted greening projects in areas like Fuxing Road, but evaluations suggest that inadequate vegetation placement and species selection have limited their effectiveness.
한중 협력: 청천 계획의 진전
Sino-Korean Cooperation: Progress in the Blue Sky Plan
중국과 한국은 '청천 계획'을 통해 대기오염 및 기후변화에 공동 대응하기로 했으며, 정책과 기술 교류, 공동 연구 등을 진행 중임.
China and South Korea have agreed to jointly address air pollution and climate change through the "Blue Sky Plan," engaging in policy and technology exchanges as well as collaborative research.
미세먼지가 중국 내 농업에 미치는 영향
The Impact of Fine Dust on Agriculture in China
미세먼지는 시설재배 작물 생육 저하 및 수량 감소를 초래하며 농작물 재배시설 외부 피복재에 부착되면 일조량 감소로 이어짐. 이에 따라 세척기술 및 보광기술 연구가 진행되고 있음.
Fine dust reduces the growth and yield of crops cultivated in facilities and adheres to external coverings of agricultural structures, leading to decreased sunlight exposure. As a result, research on cleaning technologies and supplemental lighting techniques is underway.
장단점과 주의사항
Advantages, Disadvantages, and Considerations
장점
Advantages
- 대기질 개선으로 국민 건강 증진
- Improved air quality enhances public health
- 청정 에너지 산업 육성으로 경제 성장 동력 확보
- Development of clean energy industries secures economic growth drivers
- 국제 사회에서 환경 책임 국가로서 이미지 제고
- Enhances China's image as an environmentally responsible nation on the global stage
- 주변국과 환경 협력 강화로 외교적 이점 확보
- Strengthens environmental cooperation with neighboring countries, yielding diplomatic benefits
단점 및 주의사항
Disadvantages and Considerations
- 석탄 의존도 감소에 따른 에너지 안보 문제
- Reducing coal dependence may pose energy security challenges
- 산업구조 조정으로 경기 침체 가능성
- Industrial restructuring could lead to economic stagnation
- 지역별 불균형 발전 심화 가능성
- Uneven regional development may worsen
- 막대한 재정 부담 발생 가능성
- Significant financial burdens may arise
특히 에너지 안보 문제는 석탄 사용 패턴으로 인해 지속적으로 주목받고 있음.
Energy security issues continue to draw attention due to persistent coal usage patterns.
마무리 생각
Final Thoughts
2025년 중국의 미세먼지 문제는 정부의 야심찬 목표에도 불구하고 여전히 심각한 상황임. 자연적 요인과 인위적 요인이 복합적으로 작용하고 있으며, 장기적으로는 다양한 정책과 국제 협력이 결실을 맺을 가능성이 있음.
China's fine dust problem in 2025 remains severe despite the government's ambitious goals. Both natural and human-induced factors are at play, but long-term efforts through diverse policies and international cooperation could potentially yield meaningful results over time.
더 알아보면 좋을 키워드
Keywords Worth Exploring Further
미세먼지 저감을 위한 도시 계획, 그린 인프라(Green Infrastructure), 탄소 중립(Carbon Neutrality), 대기질 모니터링 시스템, 황사 예보 시스템, 기후변화와 미세먼지의 상관관계
Urban planning for fine dust reduction, Green Infrastructure, Carbon Neutrality, Air quality monitoring systems, Sandstorm forecasting systems, Relationship between climate change and fine dust

댓글
댓글 로딩 중...